Raspberry Pi & IoT: Why It's Ideal + How To Get Started
Is a tiny computer the key to unlocking the future of interconnected devices? The Raspberry Pi, a remarkably affordable and versatile single-board computer, has rapidly become a cornerstone in the world of the Internet of Things (IoT), offering a powerful platform for innovation and experimentation.
The digital landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, with everyday objects becoming increasingly interconnected. From smart home appliances to industrial machinery, devices are now capable of communicating and exchanging data, creating a vast network of intelligent systems. This is the realm of the Internet of Things (IoT), and at its heart lies the need for efficient, adaptable, and cost-effective computing solutions. The Raspberry Pi has emerged as a prime contender in this space, offering a compelling blend of features that make it an ideal choice for a wide array of IoT applications. The question of whether a Raspberry Pi can be effectively utilized as an IoT device is not just answered in the affirmative; it is, in many cases, the preferred solution, and it's easy to understand why.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Compact Size | The Raspberry Pi's diminutive form factor makes it perfect for integration into space-constrained IoT projects. |
| Low Power Consumption | Its energy efficiency is crucial for battery-powered or continuously operating IoT devices. |
| Affordability | The low cost of the Raspberry Pi allows for experimentation and deployment in projects with tight budgets. |
| Versatility | It can be used in a wide variety of applications, from smart home automation to industrial monitoring. |
| GPIO Pins | General Purpose Input/Output pins allow the Raspberry Pi to interface directly with sensors and actuators. |
| Network Connectivity | Built-in Wi-Fi and Ethernet capabilities provide seamless integration with the internet and local networks. |
| Large Community | A vast online community provides extensive support, tutorials, and pre-built projects. |
| Operating System Flexibility | Supports various operating systems, including Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian) and other Linux distributions, providing flexibility in software development. |
For those unfamiliar with the technology, the Raspberry Pi is a credit-card-sized single-board computer developed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation. It was initially designed to promote basic computer science in schools and developing countries, but its accessibility and low cost quickly made it a hit among hobbyists, engineers, and professionals. Today, the Raspberry Pi is a go-to choice for a wide variety of projects, including IoT applications. It is widely used in embedded systems, smart devices, and DIY electronics. It is a testament to its robust performance and the accessibility of its ecosystem, solidifying its position as a top choice for IoT projects.
Why exactly is the Raspberry Pi such an attractive option for IoT development? Several key factors contribute to its popularity.
One of the most compelling advantages of the Raspberry Pi is its affordability. Compared to specialized IoT devices, the Raspberry Pi offers a significantly more cost-effective computing platform. This allows developers and enthusiasts to prototype and deploy IoT solutions without the high upfront costs associated with proprietary hardware. This is especially beneficial for those experimenting with new concepts or working on projects with limited budgets. Its compact size is another significant advantage. The Raspberry Pis small form factor makes it easy to integrate into various IoT projects, even those with space constraints. Whether its monitoring environmental conditions, controlling industrial equipment, or managing smart home devices, the Raspberry Pi can fit seamlessly into these environments.
Furthermore, the Raspberry Pi boasts impressive versatility. It can be used in a broad spectrum of applications, from home automation and data collection to device management and industrial automation. Its capabilities extend to complex tasks, such as image processing, machine learning, and serving as an IoT edge device, playing a vital role in processing and analyzing data at the edge of the network. This versatility stems from the Raspberry Pi's ability to run various flavors of Linux and perform almost all tasks that a normal desktop computer can do. The Raspberry Pi also allows interfacing sensors and actuators through the general-purpose I/O (GPIO) pins. This allows developers to interact with the physical world. Programming the Raspberry Pi with languages like Python for applications like controlling outputs and reading inputs from pins is straightforward. This simplifies the process of designing and building IoT devices, making it a simple and flexible approach.
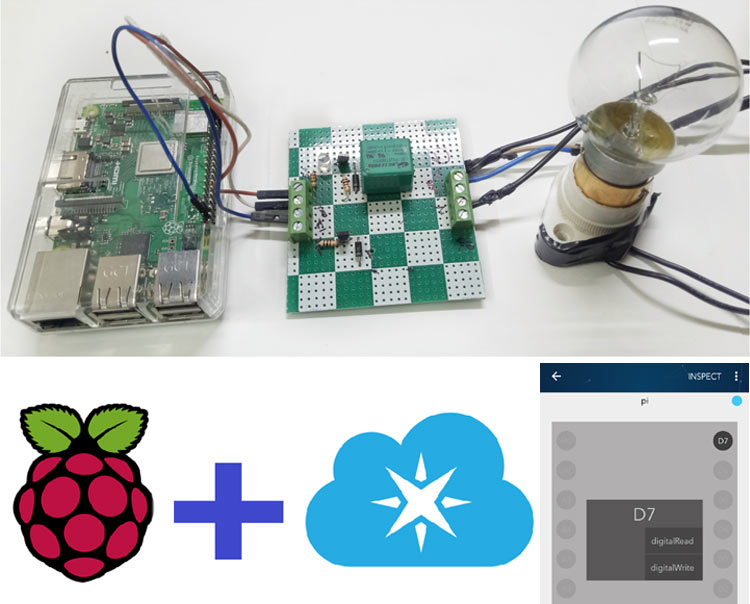
The Raspberry Pi also shines in network connectivity, a crucial feature in the IoT landscape. It provides built-in Wi-Fi and Ethernet capabilities, allowing seamless integration with the internet and local networks. This enables the Raspberry Pi to connect to cloud services, send and receive data, and communicate with other devices on the network. The Raspberry Pi also provides 8 I/O pins, which are digital in nature. To interact with other devices, an additional chip would be required to be wired to the digital pins.
The ecosystem surrounding the Raspberry Pi is also a significant asset. It benefits from a large and active community of users and developers who provide extensive support, tutorials, and pre-built projects. This community-driven support network makes it easier for both novices and professionals to get started and troubleshoot issues, fostering a collaborative environment that accelerates innovation. The Raspberry Pi Foundation itself provides extensive documentation and resources, making it even easier to learn and experiment with this versatile platform. The availability of various operating systems further expands the Raspberry Pi's capabilities.
Beyond its core functionality, the Raspberry Pi can also serve as an IoT edge device. This is where the Raspberry Pi processes and analyzes data at the edge of the network, closer to the source of the data, which reduces latency and conserves bandwidth. This is a significant advantage in applications where real-time processing is critical, such as industrial automation, environmental monitoring, and autonomous systems. The Raspberry Pi can also act as an IoT gateway, facilitating communication between different devices and protocols, further enhancing its role in the IoT ecosystem. Raspberry Pi has become a top choice for IoT (Internet of Things) projects due to its compact size, low power consumption, affordability, and versatility. Furthermore, mainstream PCs can be used as an IoT device, but doing so would prove difficult as PCs require mains power of many hundreds of watts.
Consider the practical application of Raspberry Pi in home automation. The Raspberry Pi's versatility as an IoT gateway opens up endless possibilities for home automation, data collection, and device management. You can create a home automation hub by connecting sensors to monitor temperature, humidity, and light levels, and actuators to control lighting, appliances, and other devices. The Raspberry Pi can also collect and analyze data from these sensors, providing valuable insights into your home's energy consumption and environmental conditions. By following setup guidelines and security measures, you can create a reliable and efficient IoT hub for your projects.
One of the most exciting aspects of using the Raspberry Pi for IoT projects is the learning opportunity it provides. It helps to learn about the intersection of the internet and physical objects. The Raspberry Pi's affordability and ease of use make it an ideal platform for experimenting with new technologies and developing innovative solutions. As a cheap, highly capable board with a large and active community, the Raspberry Pi is well suited to both the novice and the professional.
To get started with your IoT project using a Raspberry Pi, you will typically need to download and install an operating system, such as Raspberry Pi OS, onto an SD card. Then, connect your Raspberry Pi to a monitor, keyboard, and mouse. From there, you can begin programming your Raspberry Pi, configuring network settings, and connecting it to sensors and actuators. The new Ubuntu appliance portfolio provides free images to help you turn your Raspberry Pi into an IoT device. Just install them to your SD card, and you have all the software you need to make a media server, get started with home automation, and more. For those who want to start with the basic concepts of IoT devices, it begins with defining IoT devices and their basic building blocks.
For integrating the Raspberry Pi into your existing infrastructure, you can consider using services like Azure IoT Hub. An IoT hub in your Azure subscription. If you don't have a hub yet, you can follow the steps in create an IoT hub. You can also create a device registered in your IoT hub. If you don't have devices in your IoT hub, follow the steps in register a device. You can even select the following button to start a Raspberry Pi online simulator.
In conclusion, the Raspberry Pi is a powerful and versatile platform that has become a cornerstone of IoT development. Its affordability, compact size, low power consumption, and versatility make it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications. Whether you're a hobbyist, a student, or a professional, the Raspberry Pi provides a fantastic opportunity to explore the exciting world of the Internet of Things and create innovative solutions that can change the world. The Raspberry Pi's extensive features make it easy to build and deploy IoT devices, making it a simple and flexible approach for beginners and experts alike. As the IoT landscape continues to grow, the Raspberry Pi is poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of connected devices.