Understanding Remote IoT VPC Price: A Complete Guide
Are you ready to unlock the secrets of RemoteIoT VPC pricing and discover how to optimize your IoT infrastructure costs?
The world of Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly expanding, creating a demand for robust and secure cloud solutions. Aws RemoteIoT VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) stands out as a powerful tool for managing IoT devices, offering a private network environment within the AWS ecosystem. However, navigating its pricing structure can feel like traversing a complex maze. Whether you're a startup aiming to deploy IoT devices or a large enterprise seeking to refine your cloud infrastructure, grasping the nuances of RemoteIoT VPC pricing is essential. This guide aims to demystify every aspect, ensuring you have the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Understanding the AWS RemoteIoT VPC Landscape
AWS RemoteIoT VPC is essentially a virtual private cloud, a secure, isolated network designed specifically for IoT applications. It allows you to connect and manage your IoT devices within a private network, offering a greater degree of control and security compared to using public networks. This specialized VPC enables organizations to securely connect their IoT devices, manage data flow, and leverage AWS services in a private, isolated environment.
Let's delve into the components that shape the overall cost of a RemoteIoT VPC. This includes the initial setup, ongoing operational expenses, data transfer costs, and the level of security and compliance requirements.
RemoteIoT VPC Price Breakdown
The cost of RemoteIoT VPC is not a monolithic figure; it's a composite of several elements. Understanding these individual components is key to budgeting effectively and ensuring your IoT deployment remains cost-efficient.
1. VPC Configuration and Setup Costs
Setting up your RemoteIoT VPC involves configuring various components, and each element carries its associated costs. While AWS doesn't charge directly for the creation of a VPC itself, you will incur expenses for the resources you provision within it. These include:
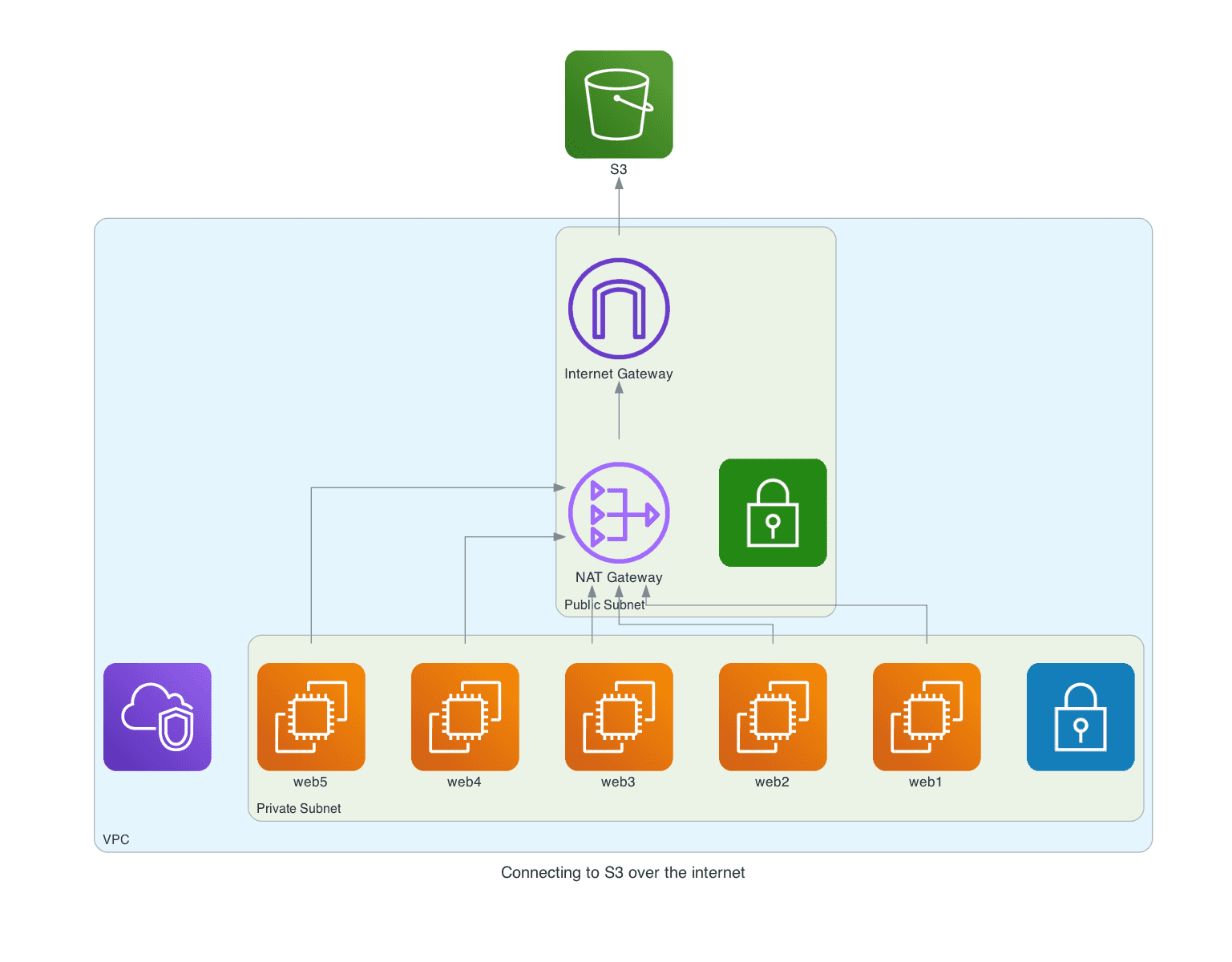
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): This is the fundamental building block, the virtual network in which you'll deploy your IoT resources.
- Subnets: You'll need to define subnets within your VPC, which are essentially subdivisions of your network. These subnets can be public (with access to the internet) or private (isolated from the internet).
- Internet Gateway: If your IoT devices or applications need to access the internet, you'll need an internet gateway, which is free, but the resources that utilize it will incur charges.
- NAT Gateway/Instances: For private subnets to access the internet, a NAT (Network Address Translation) gateway or instance is necessary. These have associated costs, with the gateway generally being more cost-effective for many use cases.
- Route Tables: These tables define how network traffic is routed within your VPC.
- Security Groups: These act as virtual firewalls, controlling inbound and outbound traffic to your instances and other resources.
- Network Access Control Lists (ACLs): ACLs provide an additional layer of security at the subnet level.
2. Instance Costs and Compute Resources
The heart of any IoT deployment lies in the instances and compute resources that process and manage data from your connected devices. The primary costs here are related to:
- EC2 Instances: You'll likely deploy Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances within your VPC to host your IoT applications, data processing services, or other compute-intensive tasks. The cost of these instances varies based on their size, type (e.g., CPU-optimized, memory-optimized), and the operating system.
- Lambda Functions: AWS Lambda functions can be used to process data from your IoT devices in a serverless manner. The pricing is based on the number of requests and the duration of the function's execution time.
- Containers (ECS/EKS): If you're containerizing your applications using Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) or Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), you'll need to factor in the costs of the underlying compute resources (EC2 instances) and the managed container services themselves.
- Other Compute Services: Depending on your specific IoT use case, you might use other compute services like AWS IoT Greengrass (for edge computing) or AWS IoT Analytics, which have their own pricing models.
3. Data Transfer Costs
Data transfer is a significant cost driver in IoT deployments. It involves the movement of data from your devices to the cloud and within your VPC. Key cost elements include:
- Data Ingress (from IoT devices): Data transferred from your IoT devices to AWS (e.g., via MQTT or HTTP) will generally incur charges.
- Data Egress (out of AWS): Transferring data from your VPC to the internet or to other AWS regions will incur data transfer charges. These charges are usually higher than data ingress charges.
- Data Transfer within VPC: Data transfer between resources within your VPC is typically free within the same Availability Zone. However, inter-Availability Zone data transfer will incur charges.
- Data Transfer to Other AWS Services: If your IoT applications integrate with other AWS services (e.g., S3, DynamoDB), you'll be charged for data transfer to and from those services.
4. Storage Costs
Storing the data generated by your IoT devices is crucial for analysis, historical tracking, and various other purposes. The primary storage options in AWS include:
- Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service): S3 is a popular choice for storing large volumes of IoT data. The cost depends on the storage class (e.g., Standard, Intelligent-Tiering, Glacier), the amount of data stored, and the number of requests made to the storage.
- Amazon DynamoDB: DynamoDB is a NoSQL database that's well-suited for storing time-series IoT data. The pricing is based on provisioned read and write capacity, as well as the storage used.
- Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service): If you require a relational database for your IoT application, you can use RDS. The cost varies depending on the database engine (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL), the instance size, storage, and other factors.
5. IoT Services and Integration Costs
Leveraging AWS IoT services can greatly simplify the management and scaling of your IoT deployments, but these services have associated costs:
- AWS IoT Core: AWS IoT Core is a managed service that allows you to connect, manage, and secure your IoT devices. The pricing is based on the number of messages sent and the duration of device connections.
- AWS IoT Device Management: This service helps you manage and monitor your fleet of IoT devices, including over-the-air (OTA) updates. The cost is based on the number of devices registered and the usage of specific features.
- AWS IoT Analytics: This service enables you to analyze and visualize your IoT data. The pricing is based on the data processed, the storage used, and the queries performed.
- Other IoT Services: Depending on your specific needs, you may use other AWS IoT services, such as AWS IoT Events (for detecting and responding to events) or AWS IoT SiteWise (for industrial data management), each with its own pricing model.
6. Security and Compliance Costs
Security and compliance are paramount for any IoT deployment. Ensuring the security of your data and adhering to industry regulations often involves additional costs:
- IAM (Identity and Access Management): Using IAM to manage user access and permissions is essential for security. While IAM itself is free, using it effectively can involve the costs of additional services used (e.g., AWS CloudTrail for auditing).
- Encryption: Encrypting your data at rest and in transit adds an extra layer of security. AWS offers various encryption services (e.g., KMS, S3 encryption) that may have associated costs.
- Compliance Requirements: If you need to meet specific industry compliance requirements (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR), you may need to use specialized AWS services or configurations, which can incur additional costs.
- Monitoring and Logging: Implementing monitoring and logging solutions (e.g., Amazon CloudWatch, AWS CloudTrail) is essential for detecting and responding to security threats. These services have associated costs based on the amount of data processed and stored.
7. Support and Maintenance
Like any complex IT infrastructure, RemoteIoT VPC deployments require ongoing support and maintenance. This can include the costs of:
- AWS Support Plans: AWS offers various support plans (e.g., Basic, Developer, Business, Enterprise) with varying levels of support and associated costs.
- Third-Party Tools and Services: You might use third-party tools for monitoring, security, or other aspects of your IoT deployment.
- Internal IT Resources: You'll need skilled IT personnel to manage your VPC, configure resources, and troubleshoot issues.
Cost Optimization Strategies for RemoteIoT VPC
While RemoteIoT VPC offers numerous advantages, optimizing your costs is crucial for ensuring the long-term viability of your IoT deployment. Here are some effective strategies:
- Right-Sizing Instances: Carefully choose the appropriate instance types and sizes for your compute workloads. Analyze your resource utilization and scale your instances up or down as needed.
- Reserved Instances/Savings Plans: Consider using Reserved Instances or Savings Plans to reduce your EC2 instance costs. This involves committing to using instances for a specific period in exchange for significant discounts.
- Data Tiering: Implement data tiering strategies to store less frequently accessed data in lower-cost storage classes, such as Amazon S3 Glacier.
- Data Compression: Compress your data before sending it to the cloud to reduce data transfer costs and storage space.
- Efficient Data Transfer: Optimize your data transfer patterns to minimize data egress charges. Use private links, caching, and other techniques to keep data transfer costs down.
- Serverless Architectures: Leverage serverless technologies (e.g., AWS Lambda, AWS IoT Core) to reduce operational overhead and pay only for the compute resources you use.
- Monitoring and Alerting: Implement robust monitoring and alerting to track your resource usage and identify potential cost anomalies.
- Cost Optimization Tools: Utilize AWS Cost Explorer, AWS Budgets, and other cost optimization tools to analyze your spending, set budgets, and receive alerts.
- Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of your RemoteIoT VPC configuration and resource usage to identify opportunities for cost savings.
- Automation: Automate tasks such as instance scaling, resource provisioning, and security updates to improve efficiency and reduce manual overhead.
Step-by-Step Guide to Estimating RemoteIoT VPC Costs
Accurately estimating RemoteIoT VPC costs can be challenging, but by following a structured approach, you can get a reasonable estimate. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Define Your Requirements: Begin by clearly defining your IoT project's requirements. This includes the number of devices, data generation rates, data storage needs, processing requirements, security needs, and the geographic distribution of your devices.
- Choose the Right AWS Services: Based on your requirements, identify the AWS services you'll need to use, such as EC2, S3, IoT Core, DynamoDB, and Lambda.
- Estimate Resource Usage: Estimate the resources you'll need for each service. For example, for EC2, estimate the instance size, number of instances, and anticipated usage hours. For S3, estimate the amount of data you'll store and the frequency of data access.
- Use the AWS Pricing Calculator: The AWS Pricing Calculator is a powerful tool that allows you to input your estimated resource usage and calculate the estimated monthly costs. You can also use the calculator to explore different pricing options and compare costs.
- Consider Data Transfer Costs: Estimate data transfer costs based on your data transfer patterns (ingress, egress, inter-AZ).
- Add Storage Costs: Estimate storage costs based on the amount of data you'll store, the storage class you'll use, and the expected number of requests.
- Factor in Other Costs: Include any additional costs for services like AWS IoT Core, AWS IoT Device Management, and security services.
- Account for Support and Maintenance: Include the costs of AWS support plans, third-party tools, and internal IT resources.
- Review and Refine Your Estimates: Regularly review and refine your cost estimates as your project evolves. Monitor your actual usage and compare it to your initial estimates.
Real-World Examples
To better understand the practical application of RemoteIoT VPC pricing, let's examine a few real-world examples:
1. Smart Agriculture Monitoring
Scenario: A farm uses sensors to collect data on soil moisture, temperature, and humidity. This data is sent to the cloud for analysis and to trigger automated irrigation systems.
Cost Components:
- AWS IoT Core (for device connectivity and message routing)
- EC2 instances (for data processing and analysis)
- S3 (for data storage)
- Data transfer (from sensors to the cloud, and within the VPC)
Cost Optimization: Using a combination of the right-sized EC2 instances, tiered storage, and optimized data transfer patterns can significantly reduce costs.
2. Connected Car Fleet Management
Scenario: A company uses sensors to track vehicle location, performance data, and diagnostic information.
Cost Components:
- AWS IoT Core (for device connectivity and message routing)
- Amazon Kinesis (for real-time data ingestion)
- Amazon DynamoDB (for storing time-series data)
- EC2 instances (for data analytics)
- Data transfer (from vehicles to the cloud, data within the VPC, and for reporting and alerting)
Cost Optimization: The strategic use of data compression, efficient data transfer patterns, and serverless components can help control costs.
3. Industrial Automation
Scenario: A manufacturing plant uses sensors to monitor machine performance, energy consumption, and environmental conditions.
Cost Components:
- AWS IoT Greengrass (for edge computing and data pre-processing)
- AWS IoT Core (for device connectivity and message routing)
- Amazon S3 (for long-term data storage)
- Amazon RDS (for relational data storage, if required)
- Data transfer (from edge devices to the cloud, and within the VPC)
Cost Optimization: Implementing edge computing and appropriate data storage tiers can balance both processing costs and storage needs.
Advanced Considerations for RemoteIoT VPC
Security Best Practices
Implementing robust security practices is paramount when designing and deploying a RemoteIoT VPC. This includes:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Use IAM to manage user access and permissions effectively.
- Security Groups and Network ACLs: Utilize security groups and Network ACLs to control network traffic.
- Encryption: Encrypt data both at rest and in transit.
- Regular Auditing: Regularly audit your VPC configuration and access logs to identify potential security vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Employ vulnerability scanning tools to identify and mitigate potential security risks.
- Use AWS Shield: AWS Shield is a managed Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection service that safeguards applications running on AWS.
Scalability
The dynamic nature of IoT deployments necessitates scalability. Consider these points:
- Auto Scaling: Utilize auto-scaling features to automatically adjust your EC2 instance capacity based on the workload.
- Database Scaling: Choose databases that can scale to handle increasing data volumes and query loads.
- Horizontal Scaling: Design your applications to scale horizontally by adding more instances or containers.
- Service Limits: Be mindful of AWS service limits and plan accordingly. Request limit increases if needed.
Compliance
Adhering to compliance requirements is essential for many IoT deployments. Make sure you:
- Understand Compliance Needs: Identify the specific compliance requirements applicable to your industry or use case (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR).
- Leverage AWS Services: Utilize AWS services that are designed to help you meet compliance requirements.
- Implement Security Controls: Implement appropriate security controls to protect sensitive data.
- Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation of your VPC configuration, security controls, and compliance efforts.
The Raspberry Pi and RemoteIoT VPCs
The Raspberry Pi, a cost-effective, credit-card-sized device, plays a significant role in P2P (peer-to-peer) IoT networks. It can act as an intermediary, collecting data from sensors and other devices, then transmitting the data to the RemoteIoT VPC. Here's how it integrates:
- Connectivity: The Raspberry Pi can be configured to connect to the RemoteIoT VPC via a secure connection, using either wired or wireless network.
- Data Collection: Equipped with GPIO pins, the Raspberry Pi can interface with various sensors, collecting real-time data.
- Data Processing: The Raspberry Pi's processor can perform some local data processing, like filtering, aggregating, and transforming sensor data before sending it.
- Security: To establish secure connections, you can use encryption protocols and manage SSH keys to establish secure communication with the RemoteIoT VPC, ensuring data privacy.
The Future of RemoteIoT VPC Pricing
AWS continually evolves its services, which will reflect in RemoteIoT VPC pricing. Keep a lookout for:
- New Pricing Models: AWS may introduce new pricing models or discounts.
- Service Updates: New features will impact the price of the available AWS services.
- Eco-Friendly Computing: AWS is making more and more of their hardware and data centers eco-friendly.
Conclusion
Successfully managing RemoteIoT VPC pricing involves a combination of understanding its various components, implementing cost optimization strategies, and regularly monitoring your resource usage. By following the guidelines and examples outlined in this article, you can build a secure, scalable, and cost-effective IoT infrastructure within the AWS ecosystem. Remember, the key is to be proactive, continuously evaluate your costs, and adapt your strategies as your IoT deployment evolves. By doing so, you can stay ahead of the curve, maximizing the benefits of your IoT initiatives while ensuring they remain financially sustainable.